Climate change is calling for various and multiple approaches in the adaptation of cities and mitigation of the coming changes. Because buildings (residential and commercial) are responsible of about 40% of energy consumption, it is necessary to build more energy efficient ones, to decrease their contribution to greenhouse gas emissions.
But what is the relation with the atmosphere. It is two folds: firstly, in a previous post, I have already described what is the impact of the buildings / obstacles on the air flow and on the air temperature. Secondly, the fact that the climate or surrounding environment is influenced, there will be a significant change in the energy consumption of these buildings. Currently, building energy simulation tool are using data usually gathered outside of the city and hence not representative of the local context. Thus it is crucial to be able to have necessary tools that capture both the dynamics of the atmosphere and also those of a building to design better and more sustainable urban areas.
In the present work, we have brought these two disciplines together by developing a multi-scale model. On the one side, a meteorological model, the Canopy Interface Model (CIM), was developed to obtain high resolution vertical profile of wind speed, direction and air temperature. On the other hand, an energy modelling tool, CitySim, is used to evaluate the energy use of the buildings as well as the irradiation reaching the buildings.
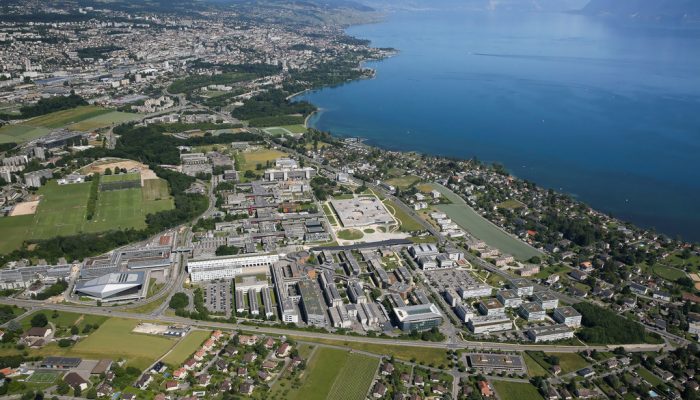
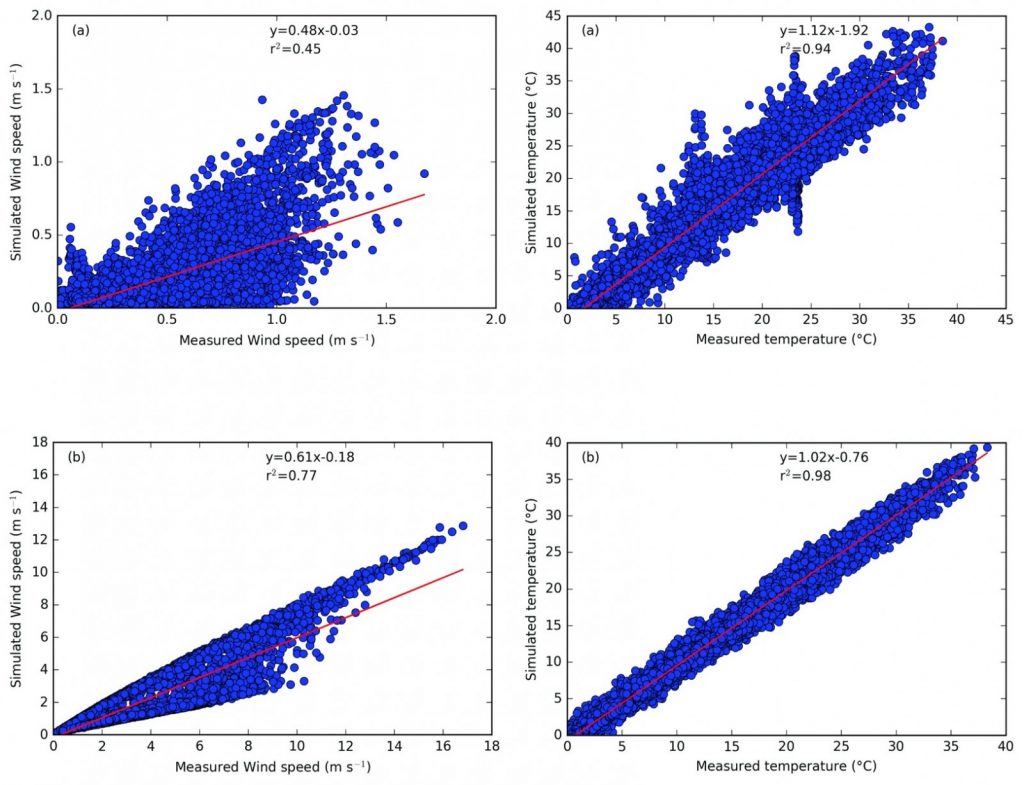
With this coupling methodology setup we have applied it on the EPFL campus, in Switzerland. We have compared the modelling results with data collected on the EPFL campus for the year 2015. The results show that the coupling lead to a computation of the meteorological variables that are in very good agreement. However, we noted that for the wind speed at 2m, there is still some underestimation of the wind speed. One of the reason for this is that the wind speed close to the ground is very low and there is a higher variability at this height.
We intend to improve this by developing new parameterization in the future for the wind speed in an urban context by using data currently being acquired in the framework of the MoTUS project. One surprising result from this part of the study, is the appearance inside of an urban setup of a phenomena call Cold Air Pools which is very typical of valleys. The reason for this is the lack of irradiation reaching the surface inside of dense urban parts.
Furthermore, we have seen some interesting behaviour in the campus for some particular buildings such as the Rolex Learning Center. Buildings with different forms and configuration, reacted very differently with the local and standard dataset. We designed a series of additional simulation using multiple building configuration and conducted a sensitivity analysis in order to define which parameters between the wind speed and the air temperature had a more significant impact on the heating demand (see Figure 1). We showed that the impact of a reduction of 1°C was more important than a reduction of 1m s-1.

Figure 1. Heating demand of the five selected urban configurations (black dots), as function of the variation by +1°C (red dots) and -1°C (blue dots) of the air temperature, and by +1.5 m s-1 (violet dots) and -1.5 m s-1 (orange dots).
Finally, we also analysed the energy consumption of the whole EPFL campus. When using standard data, the difference between the simulated and measured demand was around 15%. If localized weather data was used, the difference was decreased to 8%. We have thus been able to reduce the uncertainty of the data by 2. The use of local data can hence improve the estimation of building energy use and will hence be quite important when building become more and more efficient.
Reference / datasets
The paper (Mauree et al., Multi-scale modelling to evaluate building energy consumption at the neighbourhood scale, PLOS One, 2017) can be accessed here and data needed to reproduce the experiment are also available on Zenodo.